Khalid Adan
Software developer
Let's get synthwave-y

Let's get synthwave-y image
Picture this: neon hues in a gradient dance, and letters that look like they're straight from the 80s, morphing before your very eyes like a synthwave dream. That's right, we're getting synthwave-y and adding some dynamism to our text with a dash of React Hooks magic.
Today we'll walk through a custom React Hook, useAnimatedText, which adds an animated effect to our text.
Ready? Get in the mood with some synthwave tunes:
Synthwave Tunes
The Hook
To begin, we’ll start with a brief overview of the hook. The useAnimatedText is a function that takes an options object as a parameter. This options object contains the totalIterations property. This property determines the number of iterations our animation will take to transform each character in the text.
interface UseAnimatedTextOptions {
totalIterations: number;
}
const useAnimatedText = (
options: UseAnimatedTextOptions
): [React.RefObject<HTMLHeadingElement>, boolean] => {
// ... implementation details will follow
};
The useAnimatedText hook returns an array. The first item is a reference to the HTML element we want to animate, and the second is a boolean state indicating if the animation is currently running.
Setting The Stage With useEffect
The key player of our operation is the useEffect hook. We're using it to control the lifecycle of our animation, starting, stopping, and cleaning it up when necessary.
useEffect(() => {
// ... we will explore this in detail later
}, [options?.totalIterations]);
The useEffect hook runs whenever the totalIterations option changes. It's the controller that kicks off or restarts our text transformation.
Transforming The Text
Within our useEffect hook, we set up an interval that will iterate over each character of the text and transform it into a random letter. The speed of this transformation is determined by the totalIterations option.The idea is to convert each character of our text into a random character from this string, creating a dynamic, morphing effect. To do this, we're making use of a simple string containing all the characters of the English alphabet.
const letters = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz";
Now, the speed and scope of this transformation are governed by the totalIterations option. Let's explore how it works in the setInterval function within our useEffect hook:
intervalRef.current = window.setInterval(() => {
setIsAnimating(true);
element.innerText = element.innerText
.split("")
.map((_, index) => {
if (index < iteration) {
return text[index];
}
return letters[Math.floor(Math.random() * 26)];
})
.join("");
// ... more code follows
}, 40);
Here, we're taking our text, splitting it into an array of characters, and mapping over each character. If the index of a character is less than our iteration variable, we leave the character as is. However, if the index is equal to or greater than the iteration, we transform it into a random letter.
Our iteration variable starts at zero and incrementally increases by 1 / (options?.totalIterations ?? 3) with each interval. This essentially means that the higher the totalIterations value, the slower our animation will be.
Let's illustrate with an example: if our totalIterations is set to 5, the increment per interval would be 1 / 5 = 0.2. So, on the first interval, we'd transform 20% of our text, then 40% on the second interval, 60% on the third, and so on until 100% of the text has been transformed.
Once all characters of the text have been animated (when iteration equals or surpasses the text length), we clear the interval and set isAnimating to false, indicating that the animation is complete.
if (iteration >= text.length) {
clearInterval(intervalRef.current);
setIsAnimating(false);
}
This way, we ensure our text transformation takes exactly as many steps as we want it to, giving us control over the pace of the animation. And that's how we use totalIterations to govern the rhythm of our 80s vibe transformation!
Tidying Up: Clean Up on Unmount
When a component using this hook unmounts, it's necessary to clean up our interval to prevent memory leaks. This is done in the cleanup function returned by useEffect.
return () => {
clearInterval(intervalRef.current);
setIsAnimating(false);
};
Putting It All Together
Here's how all the pieces come together:
-
Initialize: Our hook starts by setting up a ref for our text element (elementRef), an interval ref (intervalRef), and an isAnimating state.
-
Kickoff the Animation: The useEffect hook triggers as soon as our component renders (or totalIterations changes), clearing any existing intervals before setting up a new one.
-
Perform the Transformation: The hook transforms a portion of the text into random letters in each interval, governed by the totalIterations option.
-
End the Animation: Once the text has been fully transformed, the hook clears the interval and sets isAnimating to false.
-
Cleanup: When the component unmounts, our hook clears any remaining intervals and sets isAnimating to false.
All these elements harmonize to create a dynamic and lively animation. Just import useAnimatedText, pass in your desired totalIterations, and watch as your text springs to life!
export default useAnimatedText;
That's all it takes to give your text the synthwave twist it deserves. Now, go forth and make the web a more dynamic, vibrant, and exciting place!
Here's a gif of the final result on my /blogs page:
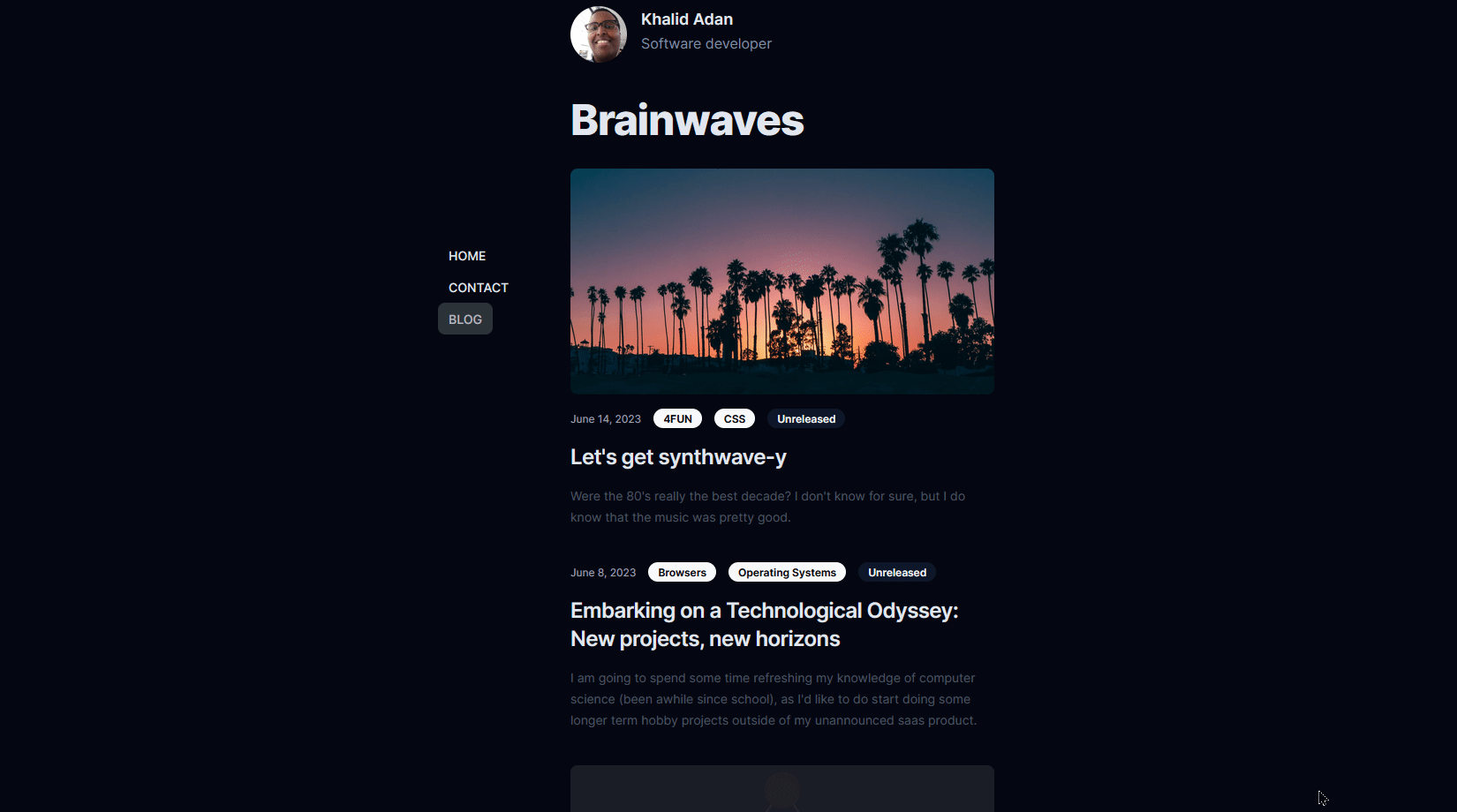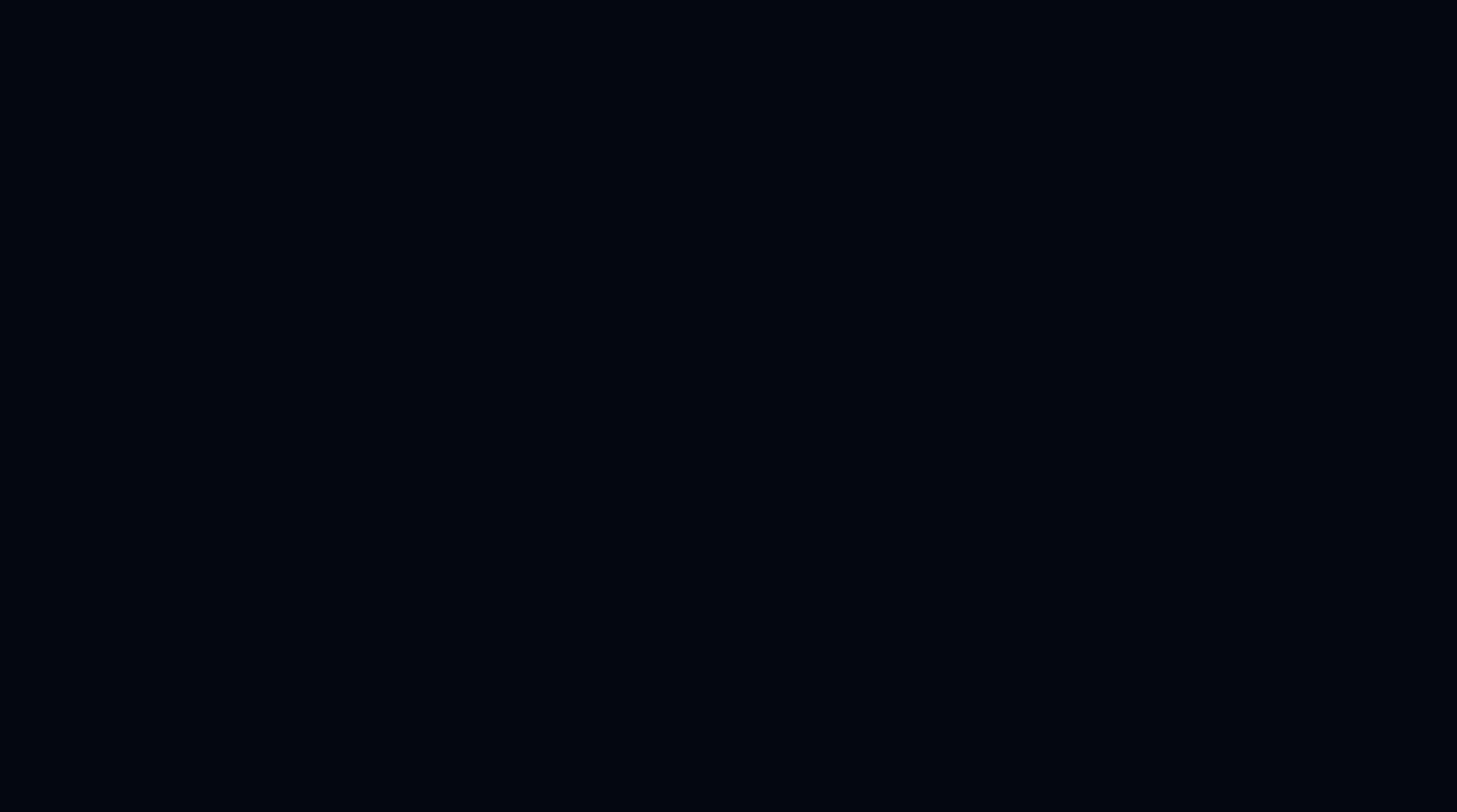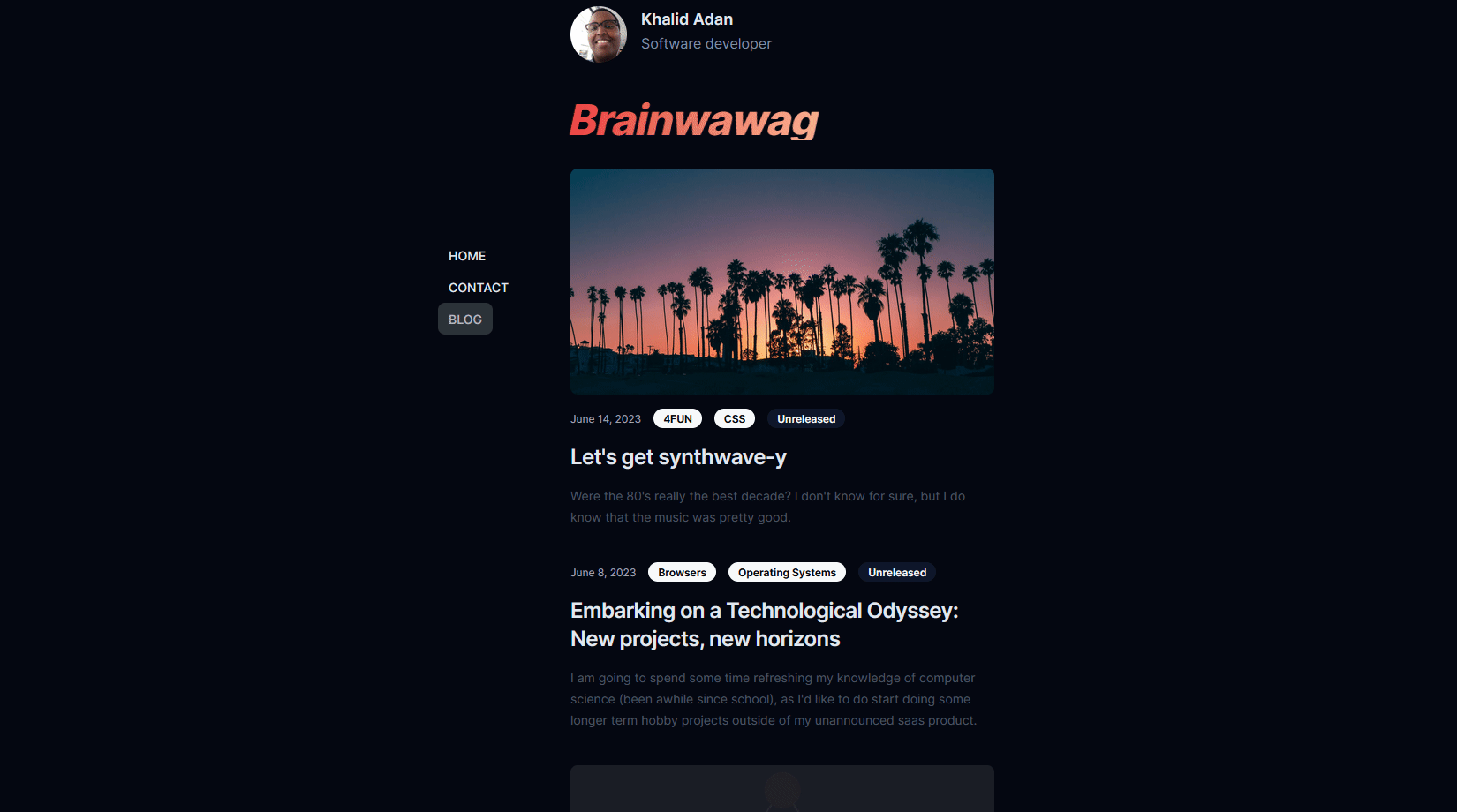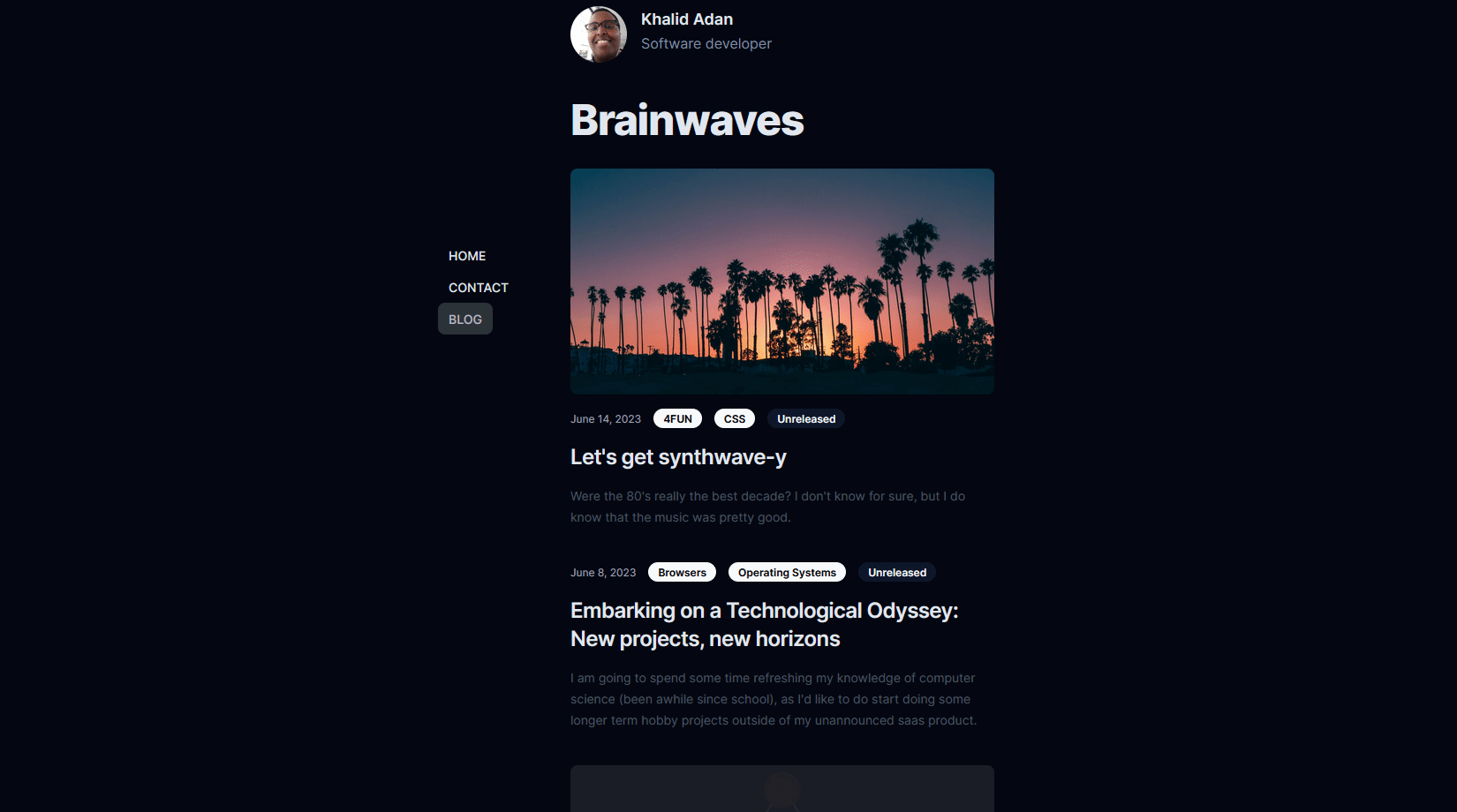
Source code
import { useEffect, useRef, useState } from "react";
interface UseAnimatedTextOptions {
totalIterations: number;
}
const useAnimatedText = (
options: UseAnimatedTextOptions
): [React.RefObject<HTMLHeadingElement>, boolean] => {
const letters = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz";
const intervalRef = (useRef < number) | (undefined > undefined);
const elementRef = useRef < HTMLHeadingElement > null;
const [isAnimating, setIsAnimating] = useState(false);
const totalIterations = options?.totalIterations ?? 3;
useEffect(() => {
const element = elementRef.current;
if (!element) {
return;
}
const text = element.innerText;
const textLength = text.length;
let iteration = 0;
clearInterval(intervalRef.current);
const animate = () => {
setIsAnimating(true);
let newText =
text.substring(0, iteration) + getRandomLetters(textLength - iteration);
element.innerText = newText;
if (iteration >= textLength) {
stopAnimation();
}
iteration += 1 / totalIterations;
};
const getRandomLetters = (num: number) => {
let result = "";
for (let i = 0; i < num; i++) {
result += letters[Math.floor(Math.random() * 26)];
}
return result;
};
const stopAnimation = () => {
clearInterval(intervalRef.current);
setIsAnimating(false);
};
intervalRef.current = window.setInterval(animate, 40);
return stopAnimation;
}, [totalIterations]);
return [elementRef, isAnimating];
};
export default useAnimatedText;
© KHLD.DEV 2025.